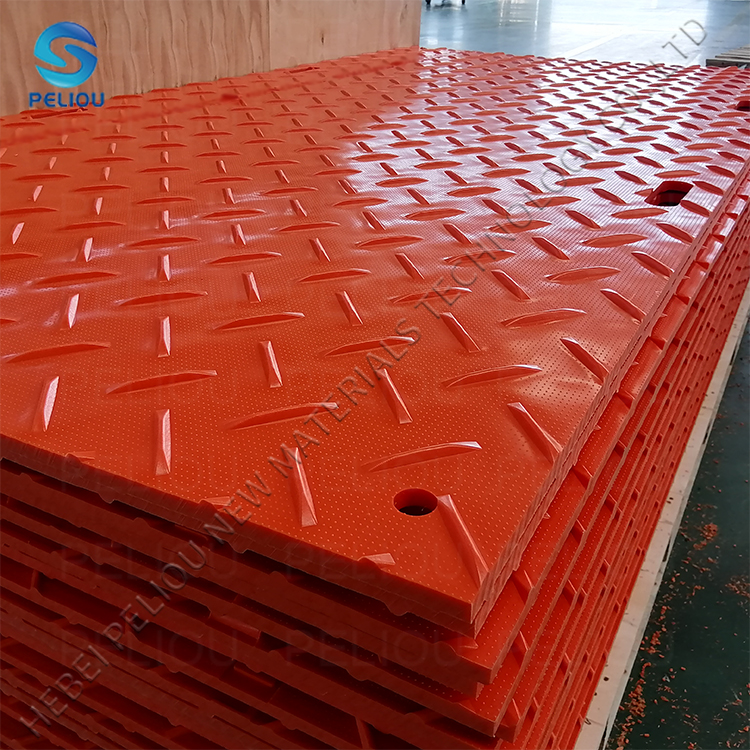
Simply put, ground protection mats do not have a fixed service life, ranging from 1-2 years to over 10 years, depending mainly on the material, usage environment, and maintenance methods.
Core factor one: Material type
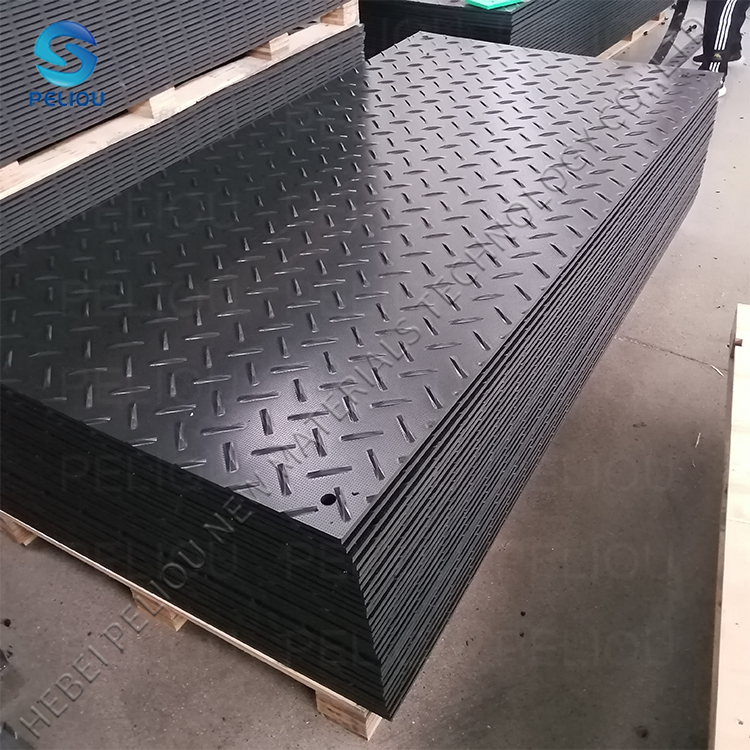
Composite material mats (polyethylene PE)
This is currently the most commonly used type, usually with a non slip texture on the surface.
Typical lifespan: 5 to 10 years or more (with proper use and maintenance).
Advantages: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant (resistant to water, oil, and chemicals), UV resistant, and will not rot or rust.
Even the best cushion can quickly be damaged if used improperly.
Load type and frequency:
Light load (pedestrian, small car, ATV all terrain vehicle): minimal wear and tear.
Heavy load (repeated crushing by excavators, loaders, and heavy trucks): causing enormous pressure and wear.
Static load (supporting cranes, temporary platforms): less wear than dynamic compaction.
Ground conditions:
Soft and muddy ground: The cushion will slightly sink, which helps to disperse the load and protect the cushion itself, making it the most ideal environment for use.
Hard and rough ground: such as rocks, asphalt pavement. The ground will wear down the bottom of the mat like sandpaper as it moves or vehicles pass by, dramatically shortening its lifespan.
Installation and handling methods:
Dragging is the primary cause of damage to mats, especially composite mats, which can tear apart the connecting rings. Forklifts or professional cushion handlers should be used for movement.
Proper installation ensures that the pads are tightly interlocked, which can evenly distribute the load and avoid damage to a single pad due to overload.
Maintenance and storage:
Cleaning: Remove heavy soil and debris after use to facilitate inspection of damage and prevent mats from sticking together.
Storage: Stacking it flat in a cool and dry place (especially avoiding direct sunlight on rubber pads) can significantly extend its lifespan.
